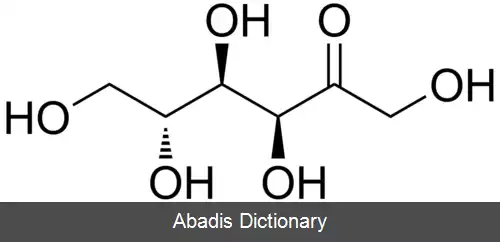
فروکتوز یا فروکتُز ( به انگلیسی: Fructose ) که از آن با نام قند میوه هم یاد می شود، از خانواده کربوهیدرات ها است که در بسیاری از میوه ها و گیاهان یافت می شود. از این ماده به عنوان شیرین کننده در صنایع مختلف غذایی و دارویی استفاده می شود به عنوان جایگزین ساکارز استفاده می شود. فرایند تولید شربت فروکتوز به این صورت می باشد که ابتدا نشاسته ذرت خالص سازی می شود و سپس با استفاده از آنزیم های آمیلازی به دکستروز تبدیل می شود و نهایتاً با عبور دکستروز از ستون های حاوی آنزیم گلوکز ایزومراز شربت فروکتوز تولید می شود که این شربت بر اساس درصد مونوساکارید فروکتوز به دو صورت ۴۲ و ۵۵ درصد عرضه می گردد.
High Fructose Corn Syrup = HFCS
فروکتوز ممکن است به شکل بی هوازی توسط مخمر یا باکتری تخمیر شود. آنزیم های مخمر، می توانند گلوکز یا فروکتوز را به اتانول و کربن دی اکسید تخمیر کنند. کربن دی اکسید آزاد شده به شکل محلول در آب باقی مانده و به تعادل با اسید بی کربنیک می رسد. البته بعد از بازکردن تانکر تخمیر، کربن دی اکسید تولید شده به هوا آزاد می شود.
فروکتوز مونوساکاریدی احیاکننده می باشد که به خوبی در واکنش میلارد شرکت می کند و با ایجاد رنگ قهوه ای مناسب در سطح محصولات نانوایی مانند کیک، کلوچه، نان و… قابلیت کاربرد زیادی در این صنایع دارد.
درصورتی که شربت فروکتوز در تماس با مخمرها یا هرگونه میکروارگانیسم دیگری قرار گیرد، به دلیل وجود دیواره سلولی نسبتاً نفوذپذیر، این شربتها قادرند آب موجود در درون سلول را به بیرون کشیده و ارگانیسم را دهیدراته نمایند. این مکانیسم مهم ترین اثر نگهدارندگی این شربت محسوب می شود. فشار اسمزی ایجاد شده توسط شربتهای قندی، با وزن مولکولی آن ها مرتبط بوده و وزن مولکولی پائینتر فشار اسمزی بیشتری ایجاد می کند. فشار اسمزی ایجاد شده توسط محلول ۱۰٪ شکر، شربت گلوکز با ۴۲=DE، دکستروز، HFCS - 90، HFCS - 55 و HFCS - 42 ( به ترتیب با وزن مولکولی ۳۴۲، ۴۲۹، ۱۸۰، ۱۸۲، ۱۸۵ و ۱۹۰ ) به ترتیب ۲/۷، ۷/۵٬۷/۱۳، ۵/۱۳، ۳/۱۳ و ۹/۱۲ می باشد. از آنجائی که HFCS مخلوطی از دکستروز و فروکتوز می باشد، به دلیل وزن مولکولی پائین و حلالیت بالا، دارای خاصیت خود - استریل کنندگی می باشد و به همین دلیل میزان مصرف مواد نگهدارنده را کاهش می دهد.
مطالعات نشان می دهد استفاده از فروکتوز در کنار سایر شیرین کننده ها مثل ساکاروز ( شکر ) ، آسپارتام و . . باعث شیرین تر شدن اجزای سازندهٔ این ترکیب می شود. [ ۳]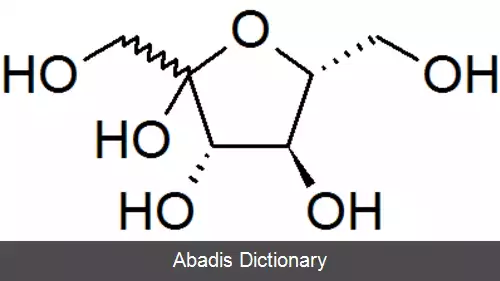
این نوشته برگرفته از سایت ویکی پدیا می باشد، اگر نادرست یا توهین آمیز است، لطفا گزارش دهید: گزارش تخلفHigh Fructose Corn Syrup = HFCS
فروکتوز ممکن است به شکل بی هوازی توسط مخمر یا باکتری تخمیر شود. آنزیم های مخمر، می توانند گلوکز یا فروکتوز را به اتانول و کربن دی اکسید تخمیر کنند. کربن دی اکسید آزاد شده به شکل محلول در آب باقی مانده و به تعادل با اسید بی کربنیک می رسد. البته بعد از بازکردن تانکر تخمیر، کربن دی اکسید تولید شده به هوا آزاد می شود.
فروکتوز مونوساکاریدی احیاکننده می باشد که به خوبی در واکنش میلارد شرکت می کند و با ایجاد رنگ قهوه ای مناسب در سطح محصولات نانوایی مانند کیک، کلوچه، نان و… قابلیت کاربرد زیادی در این صنایع دارد.
درصورتی که شربت فروکتوز در تماس با مخمرها یا هرگونه میکروارگانیسم دیگری قرار گیرد، به دلیل وجود دیواره سلولی نسبتاً نفوذپذیر، این شربتها قادرند آب موجود در درون سلول را به بیرون کشیده و ارگانیسم را دهیدراته نمایند. این مکانیسم مهم ترین اثر نگهدارندگی این شربت محسوب می شود. فشار اسمزی ایجاد شده توسط شربتهای قندی، با وزن مولکولی آن ها مرتبط بوده و وزن مولکولی پائینتر فشار اسمزی بیشتری ایجاد می کند. فشار اسمزی ایجاد شده توسط محلول ۱۰٪ شکر، شربت گلوکز با ۴۲=DE، دکستروز، HFCS - 90، HFCS - 55 و HFCS - 42 ( به ترتیب با وزن مولکولی ۳۴۲، ۴۲۹، ۱۸۰، ۱۸۲، ۱۸۵ و ۱۹۰ ) به ترتیب ۲/۷، ۷/۵٬۷/۱۳، ۵/۱۳، ۳/۱۳ و ۹/۱۲ می باشد. از آنجائی که HFCS مخلوطی از دکستروز و فروکتوز می باشد، به دلیل وزن مولکولی پائین و حلالیت بالا، دارای خاصیت خود - استریل کنندگی می باشد و به همین دلیل میزان مصرف مواد نگهدارنده را کاهش می دهد.
مطالعات نشان می دهد استفاده از فروکتوز در کنار سایر شیرین کننده ها مثل ساکاروز ( شکر ) ، آسپارتام و . . باعث شیرین تر شدن اجزای سازندهٔ این ترکیب می شود. [ ۳]


wiki: فروکتوز
