نیاایلامی یا آغازایلامی ( به انگلیسی: Proto - Elamite ) دوره ای از تاریخ ایلام میان سال های ۳۲۰۰ تا ۲۷۰۰ پیش از میلاد است. البته تا ۳۴۰۰ و ۳۵۰۰ پیش از میلاد نیز تخمین زده میشود. این دوره که معادل با اواخر دوره بانش است ، با نام شوش سوم نیز شناخته می شود.
... [مشاهده متن کامل]
برخی از مردم شناسان، مانند جان آلدن، فلیپ کهل، فرانسوا والا و دیگران، معتقدند که نفوذ نیا - ایلامیان در پایان هزاره چهارم قبل از میلاد به سرعت رشد کرد و باعث ایجاد گستره آن با سبک های مشترک در سرامیک، هنر و معماری و کنترل آن بر راه های تجاری عمده میان فلات ایران و میان رودان شد و با ایجاد تجارت دریایی در خلیج فارس چندین قرن بعد به همان سرعت کاهش یافت.
پیش - ایلامی
این دوره که شامل دو دوره ی موسوم به شوش اول و شوش دوم است، در حدود ۴۲۰۰ پیش از میلاد، آغاز شد، و در ۳۳۰۰ پیش از میلاد، پایان یافت. در این دوره بود که شوش احداث شد و اولین مهر های استوانه ای کشف شده و حکومت در دشت شوشان برپا می شود .
از حدود هزاره نهم قبل از میلاد، یک سیستم مبتنی بر نشانه در بخش های مختلف خاور نزدیک باستان مورد استفاده قرار گرفت. اینها به نشانه های علامت گذاری شده و بعداً پاکت های علامت گذاری شده، که اغلب مهر و موم نامیده می شوند، تکامل یافتند. معمولاً فرض بر این است که اینها مبنای توسعه نیا - ایلامی و همچنین نیا - میخی بوده است ( با بسیاری از نشانه ها، حدود ۲/۳، در شوش یافت شده است ) . توکن ها پس از توسعه نیا - میخی و نیا - ایلامی در استفاده باقی ماندند.
اولین لوح های یافت شده در این منطقه از نوع "عددی" هستند که فقط فهرستی از اعداد را شامل می شوند. آنها نه تنها در شوش و اوروک، بلکه در مکان های مختلفی از جمله مکان هایی که لوح های نیا - ایلامی و نیا - میخی نداشتند، مانند تل براک، حبوبا کبیرا، و تپه حصار و گودین تپه و جبل آرودا یافت می شوند.
کهن ترین آثار بالشتک/توکن که قدمت آن به نیمه نخست هزاره پنجم پیش از میلاد می رسد و قدیمی تر از نمونه های مشابه آن در میانرودان است، در محوطه چغاآهوان در دشت شوشان یافت شده است.

... [مشاهده متن کامل]
برخی از مردم شناسان، مانند جان آلدن، فلیپ کهل، فرانسوا والا و دیگران، معتقدند که نفوذ نیا - ایلامیان در پایان هزاره چهارم قبل از میلاد به سرعت رشد کرد و باعث ایجاد گستره آن با سبک های مشترک در سرامیک، هنر و معماری و کنترل آن بر راه های تجاری عمده میان فلات ایران و میان رودان شد و با ایجاد تجارت دریایی در خلیج فارس چندین قرن بعد به همان سرعت کاهش یافت.
پیش - ایلامی
این دوره که شامل دو دوره ی موسوم به شوش اول و شوش دوم است، در حدود ۴۲۰۰ پیش از میلاد، آغاز شد، و در ۳۳۰۰ پیش از میلاد، پایان یافت. در این دوره بود که شوش احداث شد و اولین مهر های استوانه ای کشف شده و حکومت در دشت شوشان برپا می شود .
از حدود هزاره نهم قبل از میلاد، یک سیستم مبتنی بر نشانه در بخش های مختلف خاور نزدیک باستان مورد استفاده قرار گرفت. اینها به نشانه های علامت گذاری شده و بعداً پاکت های علامت گذاری شده، که اغلب مهر و موم نامیده می شوند، تکامل یافتند. معمولاً فرض بر این است که اینها مبنای توسعه نیا - ایلامی و همچنین نیا - میخی بوده است ( با بسیاری از نشانه ها، حدود ۲/۳، در شوش یافت شده است ) . توکن ها پس از توسعه نیا - میخی و نیا - ایلامی در استفاده باقی ماندند.
اولین لوح های یافت شده در این منطقه از نوع "عددی" هستند که فقط فهرستی از اعداد را شامل می شوند. آنها نه تنها در شوش و اوروک، بلکه در مکان های مختلفی از جمله مکان هایی که لوح های نیا - ایلامی و نیا - میخی نداشتند، مانند تل براک، حبوبا کبیرا، و تپه حصار و گودین تپه و جبل آرودا یافت می شوند.
کهن ترین آثار بالشتک/توکن که قدمت آن به نیمه نخست هزاره پنجم پیش از میلاد می رسد و قدیمی تر از نمونه های مشابه آن در میانرودان است، در محوطه چغاآهوان در دشت شوشان یافت شده است.


نیا ایلامی دودمان یا خاندانی هستند با بیش400 سال حکومت در دوران 2800 - 3200 سال پیش از میلاد می زیسته اند
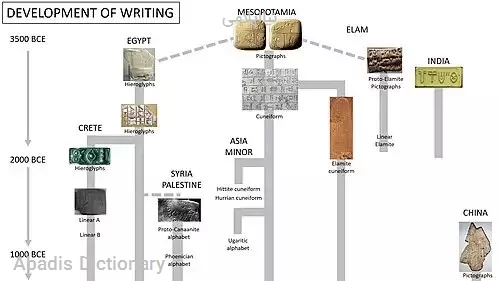
کهن ترین دبیرهٔ ایلامی که نیا - ایلامی نام گرفته، نخستین بار به سال ۲۹۰۰ پیش از میلاد در شهر شوش، پایتخت ایلامیان، در جنوب غرب ایران کار گرفه شد . گویا دبیرهٔ نیا - ایلامی گسترش یافته از دبیره میخی سومری یا دبیرهٔ باستانی سومری باشد.
... [مشاهده متن کامل]
دبیرهٔ نیا - ایلامی دارای ۱۰۰۰ نشانه است و به نظر می رسد که باید بخشی از آن واژه نگار باشد. این دبیره هنوز رمزگشایی نشده است، و زبانی را که نمایش می دهد هنوز ناشناخته است.
این یک نوشتار خُرد پیرامون ایران است. با گسترش آن به ویکی پدیا کمک کنید.
منبع [ویرایش]
مجله باستان شناسی و تاریخ، ش ۲۳، ۲۴ ، ( پاییز، زمستان ۱۳۷۶، بهار، تابستان ۱۳۷۷ ) : ص ۶ - ۹.
رده ها: تاریخ ایران خط
قس انگلیسی
The Proto - Elamite period is the time of ca. 3200 BC to 2700 BC when Susa, the later capital of the Elamites, began to receive influence from the cultures of the Iranian plateau. In archaeological terms this corresponds to the late Banesh period. This civilization is recognized as the oldest in Iran and was largely contemporary with its neighbour, Sumerian civilization, the oldest in the world, which began around 3400 BC.
The Proto - Elamite script is an Early Bronze Age writing system briefly in use for the ancient Elamite language before the introduction of Elamite Cuneiform.
Contents [show]
[edit]Overview
Clay tokens, from Susa, Uruk period, circa 3500 BC. Department of Oriental Antiquities, Louvre.
During the period 8000–3700 BC, the Fertile Crescent witnessed the spread of small settlements supported by agricultural surplus. Geometric tokens emerged to be used to manage stewardship of this surplus. [1]
The Mesopotamian civilization emerged during the period 3700–2900 BC amid the development of technological innovations such as the plough, sailing boats and copper metal working. Clay tablets with pictographic characters appeared in this period to record commercial transactions performed by the temples. [1]
Tablet with numeric signs and script. From Teppe Sialk, Susa, Uruk period ( 3200 BC to 2700 BC ) . Department of Oriental Antiquities, Louvre.
Besides Susa, one important Proto - Elamite site is Teppe Sialk, where the only remaining Proto - Elamite ziggurat is still seen. Texts in the undeciphered Proto - Elamite script found in Susa are dated to this period. It is thought that the Proto - Elamites were in fact Elamites ( Elamite speakers ) , because of the many cultural similarities ( for example, the building of ziggurats ) , and because no large - scale migration to this area seems to have occurred between the Proto - Elamite period and the later Elamites. But because their script is yet to be deciphered, this theory remains uncertain.
Some anthropologists, such as John Alden, maintain that Proto - Elamite influence grew rapidly at the end of the 4th millennium BC and declined equally rapidly with the establishment of maritime trade in the Persian Gulf several centuries later.
Proto - Elamite pottery dating back to the last half of the 5th millennium BC has been found in Sialk, where Proto - Elamite writing, the first form of writing in Iran, has been found on tablets of this date. The first cylinder seals come from the Proto - Elamite period, as well. [2]
[edit]Proto - Elamite script
Economic tablet with numeric signs. Proto - Elamite script in clay, Susa, Uruk period ( 3200 BC to 2700 BC ) . Department of Oriental Antiquities, Louvre.
It is uncertain whether the Proto - Elamite script may be considered the direct predecessor of Linear Elamite. Both scripts remain largely undeciphered, and it is mere speculation to postulate a relationship between the two.
A few Proto - Elamite signs seem either to be loans from the slightly older proto - cuneiform ( Late Uruk ) tablets of Mesopotamia, or perhaps more likely, to share a common origin. Whereas proto - cuneiform is written in visual hierarchies, Proto - Elamite is written in an in - line style: numerical signs follow the objects they count; some non - numerical signs are 'images' of the objects they represent, although the majority are entirely abstract.
Proto - Elamite was used for a brief period around 3000 BC ( presumably contemporaneous with Uruk III, or Jemdet Nasr in Mesopotamia ) , whereas Linear Elamite is attested for a similarly brief period in the last quarter of the 3rd millennium BC.
Proponents of an Elamo - Dravidian relationship have looked for similarities between the Proto - Elamite and the Indus script. [2]
[edit]Inscription corpus
The Proto - Elamite writing system was used over a very large geographical area, stretching from Susa in the west, to Tepe Yahya in the east, and perhaps beyond. The known corpus of inscriptions consists of some 1600 tablets, the vast majority unearthed at Susa.
Proto - Elamite tablets have been found at the following sites ( in order of number of tablets recovered ) :
Susa ( more than 1500 tablets )
Malyan ( more than 30 tablets )
Tepe Yahya ( 27 tablets )
Sialk ( 22 tablets )
Jiroft ( two tablets )
Ozbaki ( one tablet ) < . . .
... [مشاهده متن کامل]
دبیرهٔ نیا - ایلامی دارای ۱۰۰۰ نشانه است و به نظر می رسد که باید بخشی از آن واژه نگار باشد. این دبیره هنوز رمزگشایی نشده است، و زبانی را که نمایش می دهد هنوز ناشناخته است.
این یک نوشتار خُرد پیرامون ایران است. با گسترش آن به ویکی پدیا کمک کنید.
منبع [ویرایش]
مجله باستان شناسی و تاریخ، ش ۲۳، ۲۴ ، ( پاییز، زمستان ۱۳۷۶، بهار، تابستان ۱۳۷۷ ) : ص ۶ - ۹.
رده ها: تاریخ ایران خط
قس انگلیسی
